- Details
- Written by: Douglas Berry
- Category: Pythagorean
- Hits: 504
- Details
- Written by: Douglas Berry
- Category: Pythagorean
- Hits: 722
Mitigating Disruptive Innovation Risk
Let's begin with a defintion for innovation: Innovation is a match beween a need and a solution. Technology innovation can be brought about by inventing a new solution, discovering a new need or by improvising a new solution by applying an existing solution and need in a new way. Innovation need to create value:
- Is the need real?
- Does the solution meet the need?
- Can the solution be delivered cost effectively?
There are 3 Frontiers of innovation that corporates fall into. They need to exploit an existing technology, a new technology for an existing solution, or exploration of a completely new approach or solution. Each have their own risk reward systems with respect to adoption of the technology or solution itself.
The TekMetrix Ambidextrous Innovation Matrix, Figure below, indicates that in order to improve and sustain our business model we must fill the innovation pipeline with Frontier 3 opportunities. TekMetrix will assist our clients in identifying, developing and sustaining an innovation pipeline. We create a culture of innovation from our experience and knowledge through:
- Identifying investment needs in technology exploration
- Working to assign a central authority responsible for innovation
- Managing the innovation pipeline
- Creating a model to value the innovation
- Value Created (VC) = Function (idea, development capabilities and external factors)
- Managing a portfolio of innovation projects
- Managing the quality of ideas
- Integrating with the business units from the start
- Developing capabilities (skills, assets, systems)
We privide both an offensive and a defensive perspective on assisting our clients with innovtion. Offensive points of vew begin with how to discover and pursue opportunities for future growth and from a densive point of view how our can clients mitigate their rise to disruptive innovation. When an organization is faced with disruptive threats we work them to manage risk assisting with strategy development along the following decision scenarios:
- Fully Invest in the disruptive technology
- Invest in a project or create a new organization to mitigate, hedge against the risk of disruptive innovation
- Review anti-competitive actions
- Concede and manage for cash
- Change the game by proactively investing in new market opportunities
- Invest in Frontier 3 opportunities creating Frontier 2 opportunities
- Minimally we work with our clients to extend their business processes to enhance Frontier 2 culture and capabilities
- Taking a project portfolio perspective for Frontier 2 represents risk mitigation
- Leverage Frontier 2 opportunities to make money with at horizon 1 - exploitation
Defining the Innovation Process
- Strategy - what is the plan to proceed with innovtion efforts, what is the innovation opportunity (hypothesis)?
- Project - how to get the optimized return for specific innovation activities?
- Innovation Process - is this a new innovation process or an existing innovatino process in the client organization?
- Discovery processes to create more opportunities (workshops, innovation events, projects, partnerships)
- Find better opportunities by involving experts who have reliably generated high quality ideas in the past
- Inceasing idea quality variance by involving customers, suppliers, and other SMEs
- Creating an effective selection process
- Resolve team tension, work within productive processes
- Identifying and balancing internal versus external modes of innovation
- Details
- Written by: Douglas Berry
- Category: Pythagorean
- Hits: 633
A critical strategic activity is to determine readiness to scale the business ecosystem. Growth and scaling are not the same. Growth is defined as adding resources at the same rate as adding revenue. This occurs in services organizations such as consulting firms. Scaling is about adding revenue at an exponential rate while adding resources at an incremental rate. To scale a business ecosystem corporates must invest by taking, for example, the current quarter margin and investing it into the next quarter capturing even more revenue. For many companies growth is not a strategy. And with the proper skills and technologies it is easier than ever to scale a business ecosystem. The internet offers a myriad of ways to adversise and capital flow into marketing has been historically large. Growth as a strategy is easy to copy but more than likely a business that has a growth strategy will probably fail.
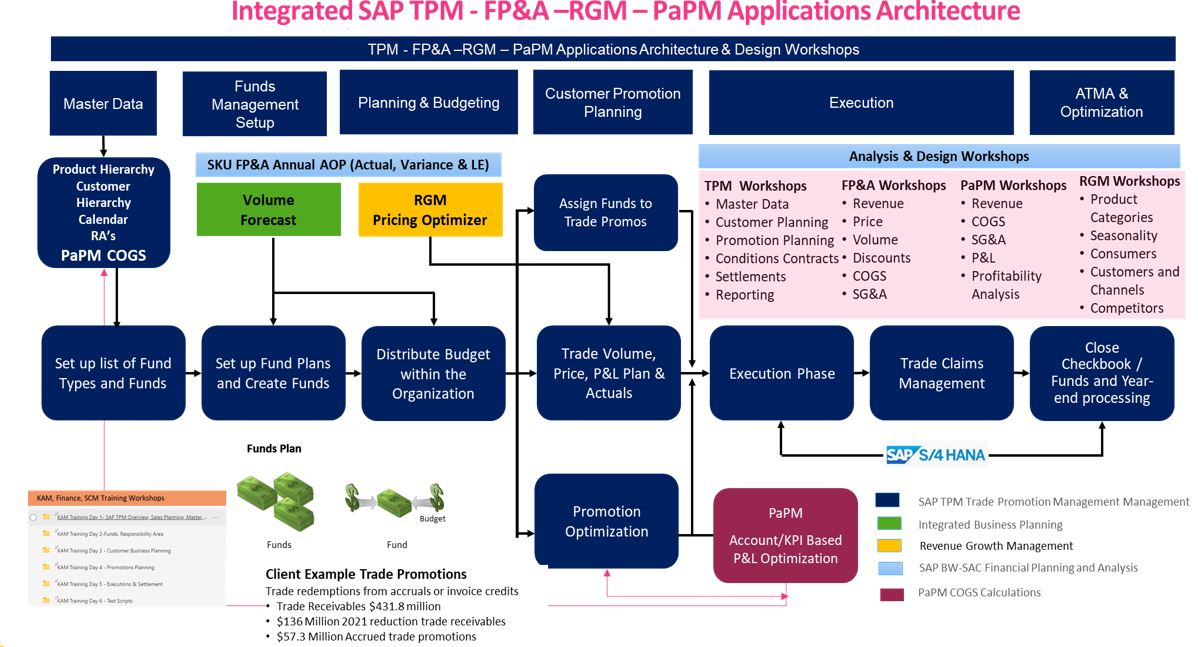
Most all organizations have a common goal: and that goal is creating value. How an organization explains and demonstrates value add to their customers, investors and or stakeholders is a key challenge. To scale a business ecosystem the company must be efficient. Successful organizations are able to develop and link measurable organizational and business metrics that are then coupled to a financial metric, creating a goal with a measurable outcome and, finally, creating and measuring the leading metrics that indicate that the organization is ready to scale the business ecosystem. TekMetrix uses the TekMetrix Value Driver Tree (VTD) data model deloyed in SAP SAC for this purpose of measuring and maintaining efficiency.
This model can be developed for each product SKU, with aggregations acrosss SAP master data and analyzed at the detailed product SKU. We use TekMetrix experience, knowledge base, AnalyticA tools and SAP SD MM FI CO COPA, BOM, Material Master, HANA SAC data models. We deploy these models using S4 BW4HANA, SAC and PaPM and Fiori. We deliver machine learning use cases on these models using regression and linear optimization algorithms creating a SKU level S&OP, AOP resulting in a newly purposed FP&A process for the enterprise.

Analyzing efficiency metrics like these above, costs per product or user, cost of revenue, revenue, loss per product or user assists in the scalability of the business ecosystem. These metrics assist the client in determining readiness to scale by making visible demand or supply side-side economics represented in their business model and ecosystem.
Supply-side economies of scale:
- Cost-based economies of scale
- Resouce pooling in supply chain and servcies
Demand-side economies of scale:
- Network effects
- Performance benefits achieved from scale
TekMetrix IT strategy components of a business ecosystem:
- Supply side economies of scale
- Demand side economies of scale
- Switching costs
- Learning curves
- Metrics
- Creating an organizational flywheel
Technology adoption and services adaptations are strategic aspects to assist in the decision and timing of scaling activities. We assist clients in codifying a process to hire, train and allow others to execute providing an appropriate division of labor by balancing people and process.
To assist an organization to scale their business we ask the following questions using the TekMetrix Synergy Framework:
- Scalable: Is the strategy, market, demand side - supply side economic business model favorable to scale?
- Constraints: What resoruces are needed, what do we have?
- Alignment: Do we have product and process market fit?
- Leadership: Do we have the right organization, leadership and employees?
- Efficiency: Do we have the know how to make money efficiently which requires a business model which is repeatable and scable?
With TekMetrix tools and leadership it is much easier to scale a business today than in the 1990s.Tools, know how, cloud compute are readily available, i.e the cost of compute, storage and cloud services have dramatically reduced.
- Details
- Written by: Douglas Berry
- Category: Pythagorean
- Hits: 730
SAP SAC Supply Chain, Value Chain, Ecosystem
The supply chain is an operational view of interconnected activities between source of materials or services, conversion of materials or services to products and services and distribution of those products and services to end customers. Key metrics are cycle times, activity changes e.g., sales order changes, conversion costs and customer satisfaction. Short term disruption in the supply chain can occur because of pricing changes due to inflation, logistics delays, or weather issues. Longer term disruption includes competitor adoption of AI, IoT, ML and blockchain technologies.
The value chain is the set of activities that a firm chooses to assemble in order to either focus on cost or provide a differentiating value proposition when going to a market.
An ecosystem is a set of external business models and assets that contribute to the focal (primary product or service offer) user’s value proposition to the end customer.
Adoption of ML technology for improved forecasting in the supply chain has been accelerating. Skills and software are the adoption factors. Also are incumbent systems where master and transaction data is of sufficient quality to be used as an input into a learning algorithm. The quality of data has improved and the ML algorithm has improved, along with comput to take as inputs on a variety of data formats and meta data types.
As for value chain activities they have been disrupted largely by the wide spread adoption of enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions. Largely all processes are automated and integrated. Organizations are slim, lean and more productive. However, they lack the adoption of existing AI technologies due to worker understanding and skills and complementary infrastructure to leverage the use of the new AI technologies.
Key Premises of an SAP SAC TPM PaPM RGM Ecosytem
- Multiple actors - different organizations contribute toward the focal offers value proposition
- Economic complementarities between actors - functions performed by the actors create or enhance the user value proposition
- For example POS data from Nielsen, IRA and SPINS provide syndicated market data
- Structural technological interdependencies between actors
- APIs connect SAP with application developers to help users benefit from from SAP data
- R, Python, Regression Analytics (volume forecasting, trade planning and forecasting, trade optimization)
- APIs connect SAP with application developers to help users benefit from from SAP data
- Product SKU level planning, forecasting, actuals and variance statistics (AOP, S&OP, Trade Promotions, Trade Executions)
- The value created by an Ecosystem is limited by its weakest link, bottlenecks
- Ecosystems and ecosystem strategy is not the same as a value chain or supply chain strategy, each are distinctly different
- Many of the worlds Ecosystems are organized around a central SAP platform
- Most of the worlds top companies have a platform based strategy for value creation (Apple, Uber, Amazon, Tesla)